Fostering Diversity in the Workplace
Fostering Diversity in the Workplace
In today's rapidly evolving workplace
landscape, fostering diversity isn't just a buzzword – it's a business
imperative. A diverse workforce brings together individuals with unique
perspectives, backgrounds, and experiences, leading to increased innovation,
creativity, and overall organizational success. In this blog, Author will
explore the importance of diversity in the workplace and discuss actionable
strategies for creating an inclusive environment where every employee can
thrive
Understanding Diversity
Diversity transcends mere
surface-level distinctions such as race, gender, and ethnicity. It encompasses
a broad spectrum of characteristics, perspectives, and experiences that shape
individuals' identities and interactions within the workplace
Beyond the visible dimensions of
diversity, there are less tangible aspects that are equally significant. These
include differences in cognitive styles, communication preferences, and
problem-solving approaches. Embracing diversity means acknowledging and valuing
these nuances, recognizing that they enrich the collective tapestry of the
organization
Diversity extends beyond
demographic categories to encompass life experiences, cultural backgrounds, and
personal beliefs. Each individual brings a unique set of influences and
insights shaped by their upbringing, education, and professional journey.
Embracing diversity involves creating an environment where these diverse
backgrounds are not only accepted but actively celebrated
Diversity encompasses differences
in physical and cognitive abilities, as well as neurodiversity. Recognizing and
accommodating these differences fosters a culture of inclusivity and
accessibility, ensuring that every individual can fully participate and
contribute to the organization's success
Embracing diversity requires a shift
in mindset – from viewing differences as obstacles to overcome to embracing
them as opportunities for growth and learning. By fostering an inclusive
culture that values and leverages diversity in all its forms, organizations can
unlock the full potential of their workforce and thrive in today's dynamic and
interconnected world
Figure 1:Strategies
for Creating a Inclusive Workplace
Source:
The Business Case for Diversity
In addition to the tangible
benefits of improved financial performance and competitive advantage, diverse
teams bring a wealth of perspectives, experiences, and ideas to the table. This
diversity of thought fuels innovation and creativity, driving organizations to
develop novel solutions to complex problems
Fostering diversity sends a
powerful message to both internal and external stakeholders about the
organization's commitment to fairness, equality, and social responsibility.
This enhances the company's reputation and brand image, attracting top talent,
customers, and investors who align with its values
Creating an Inclusive Culture
Building a truly inclusive
workplace goes beyond simply hiring a diverse workforce. It requires creating
an environment where every employee feels valued, respected, and empowered to
contribute their unique perspectives. This involves,
Implementing inclusive policies and
practices that promote fairness and equality.
Providing diversity and inclusion
training to all employees to raise awareness and foster understanding.
Encouraging open dialogue and
feedback channels where employees can voice their concerns and suggestions.
Recognizing and celebrating
diversity through events, initiatives, and cultural celebrations
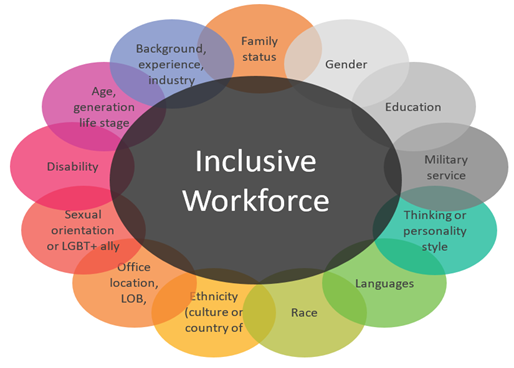
Figure 2: Inclusive
workforce
Source:
Overcoming Challenges
Despite the benefits of diversity,
organizations may face challenges in fostering an inclusive culture. Common
obstacles include unconscious bias, resistance to change, lack of leadership
commitment, and communication barriers. Addressing these challenges requires a
concerted effort from leadership, HR, and employees at all levels
Raising awareness about unconscious
bias and its impact on decision-making.
Providing diversity training and
resources to help employees recognize and mitigate bias.
Holding leaders accountable for
creating inclusive teams and environments.
Encouraging allyship and support
from all employees in championing diversity and inclusion initiatives.
Empowering Employee Resource Groups
(ERGs)
Employee Resource Groups, or ERGs,
play a crucial role in fostering diversity and inclusion within organizations.
These voluntary, employee-led groups provide a platform for employees with
shared identities or interests to connect, support one another, and advocate
for positive change. By empowering ERGs and integrating them into the broader
organizational strategy, companies can tap into the collective wisdom and
energy of their diverse workforce
Measuring Success
To evaluate the impact of diversity
and inclusion initiatives, measurable objectives need to be established and
relevant metrics tracked over time. These objectives may encompass various
aspects of organizational operations, such as workforce composition, employee
experiences, and overall company performance
Figure 3: Five key
considerations of culture groups
Source:
Conclusion
In conclusion, diversity isn't
merely viewed as a moral obligation; it's recognized as a strategic imperative
that lies at the heart of organizational success in the 21st century. By
fostering an inclusive workplace culture where every employee is valued,
respected, and empowered, the full spectrum of human potential within the
diverse workforce can be harnessed by organizations. This isn't about ticking
boxes or meeting quotas; it's about unleashing creativity, driving innovation,
and achieving sustainable growth in an increasingly interconnected and
competitive world.
Moving forward, a commitment is
made to building a future where diversity isn't just celebrated but deeply
ingrained in the fabric of organizational culture. Diversity is embraced not as
a checkbox on a to-do list but as the very essence of what makes teams
stronger, ideas more vibrant, and impact more profound. Together, a future is
envisioned where diversity isn't seen as a challenge to overcome but as the key
to unlocking unprecedented levels of success and fulfillment for all.
References
Anjum, G., 2024. Advancing Equity in Cross-Cultural
Psychology: Embracing Diverse Epistemologies and Fostering Collaborative
Practices. 2(1), pp. 17-48.
Crisp, R. J., 2011. Cognitive Adaptation to the Experience
of Social and Cultural Diversity. American Psychological Association, 137(2),
p. 242–266 .
Davidson, M., 2013. The End of Diversity as We Know It: Why
Diversity Efforts Fail and How Leveraging Difference Can Succeed. 3(1), pp.
1-27.
Dover, T. L., Kaiser, C. R. & Major, B., 2019. Mixed
Signals: The Unintended Effects of Diversity Initiatives. pp. 1-52.
Drummond, J., 2024. Corporate culture groups. [Online]
Available at: https://corporateculture.co.uk/fostering-and-promoting-a-diverse-culture-five-key-considerations/
[Accessed 23 March 2024].
Egitim, S., 2022. Challenges of adapting to organizational
culture: Internationalization through inclusive leadership and mutuality. Social
Sciences & Humanities Open, 4(1), pp. 17-88.
Ferdman, B. M., 2017. Paradoxes of Inclusion: Understanding
and Managing the Tensions of Diversity and Multiculturalism. The Journal of
Applied Behavioral Science, 53(2), pp. 235-263.
Foldy, E. G., 2021. Foldy--ERGs and Their Impact--Narrative
& table. pp. 11-45.
Green, W. M., 2018. Employee resource groups as learning
communities. 4(2), pp. 40-49.
Iancu, S., 2024. Fostering Diversity: Strategies for
Creating a Inclusive Workplace, s.l.: LinkedIn.
Mahadeo, J. D., 2012. Board Composition and Financial
Performance: Uncovering the Effects of Diversity in an Emerging Economy. J
Bus Ethics , 105(7), pp. 375-388.
Martin, N. T., 2012. Diversity and the Vir ersity and the
Virtual Workplace: P orkplace: Performance Identity and formance Identity and
Shifting Boundaries of Workplace Engagement. 18(11), pp. 605-648.
Mercer, 2024. Mercer. [Online]
Available at: https://mobilityexchange.mercer.com/insights/article/managing-a-diverse-and-inclusive-mobile-workforce
[Accessed 23 March 2024].
Podsiadlowski, A., Gröschke, D., Kogler, M. & Springer,
C., 2013. Managing a culturally diverse workforce: Diversity perspectives in
organizations. International Journal of Intercultural Relations, 37(4),
pp. 159-175.
Pless, N. M. & Maak, T., 2004. Building an Inclusive
Diversity Culture: Principles, Processes and Practice. Journal of Business
Ethics, 54(9), p. 129–147.
Wambui , T. W., Wangombe, J. G., Muthura , M. W. &
Kamau, A. W., 2013. Managing Workplace Diversity:A Kenyan Pespective. International
Journal of Business and Social Science , 16(4), pp. 199-219.






Fostering diversity in the workplace is imperative for innovation and inclusivity. By promoting diverse hiring practices, providing equitable opportunities for advancement, and fostering a culture of respect and belonging, organizations can harness the full potential of their employees and drive sustainable success.
ReplyDeleteFostering diversity in the workplace cultivates innovation and inclusivity. Through equitable hiring, promoting diverse perspectives, and fostering a culture of respect, organizations harness the full potential of their workforce.
ReplyDeleteUnity is Diversity
ReplyDelete.
ReplyDeleteAs you have clearly explained the importance of Diversity and how it plays a vital role in modern day organisations. Competitor advantages such as proper communications can be achieved resulting in positive outcomes within a organisation.
ReplyDeleteFostering diversity in the workplace requires proactive efforts to create an inclusive environment where all individuals feel valued, respected, and empowered to contribute their unique perspectives and talents. This can involve implementing diverse recruitment practices, providing training on unconscious bias, promoting cultural awareness, and fostering open communication and collaboration among employees from diverse backgrounds.
ReplyDeleteFostering diversity in the workplace requires proactive efforts to create an inclusive environment where all individuals feel valued, respected, and empowered to contribute their unique perspectives and talents. This can involve implementing diverse recruitment practices, providing training on unconscious bias, promoting cultural awareness, and fostering open communication and collaboration among employees from diverse backgrounds.
ReplyDelete